Beginning in January 2017 with the release of Chrome 56, Google will start flagging plain HTTP connections as insecure in its popular Chrome browser.
This will be the first step in a staged rollout.
Rollout Roadmap
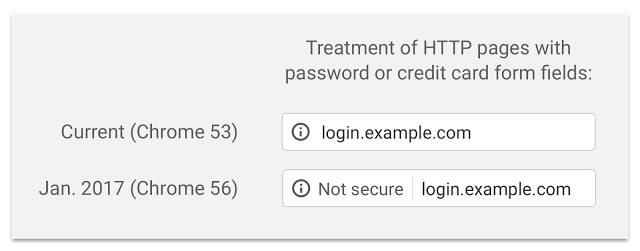
- Start flagging plain HTTP connections as non-secure for websites that contain password or credit card fields.
- Start flagging plain HTTP connections as non-secure in the privacy-oriented Incognito mode.
- Eventually show the warning for all HTTP pages and switch the security indicator to the red triangle now used for broken HTTPS connections.
Will this affect my website?
Beginning January 2017, if your website contains password or credit card fields and uses http instead of https, this will affect your website.
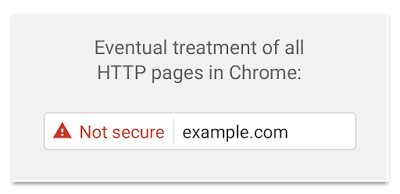
Eventually, ALL HTTP pages in Chrome will be indicated like with a red triangle (regardless of viewing mode or whether your site contains password or credit card fields).
How can I avoid my website being marked as insecure?
- Install an SSL certificate for your website. Let’s Encrypt offers free SSL certificates!
- Update your website to work with HTTPS. This step may or may not require a bit of work. Updating a website to work with HTTPS can include updating links and third-party integrations.
There is a post on the Google Developers blog that provides additional information: Avoiding the Not Secure Warning in Chrome.
Bonus SEO Boost
Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal in its search engine, so updating your website to HTTPS will not only increase security for the users of your website, but you’ll get a small boost in Google’s search engine for doing so! Win-win!